The Science of Fertility: Understanding Ovulation
Ovulation is a crucial process in a woman's reproductive cycle that determines her fertility. Understanding science behind ovulation can help individuals and couples make informed decisions regarding family planning and conception.
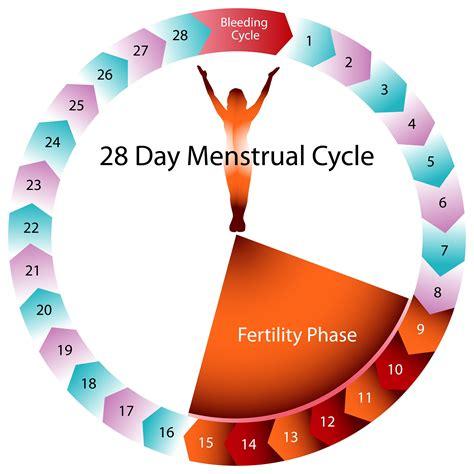
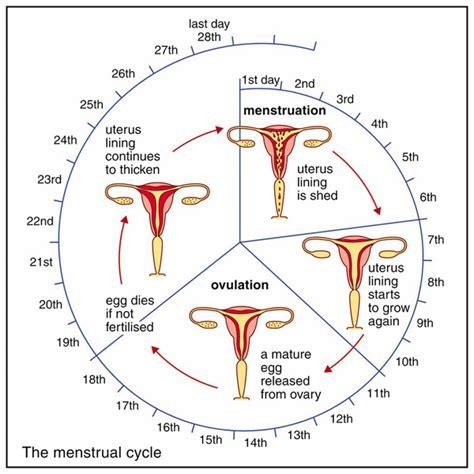
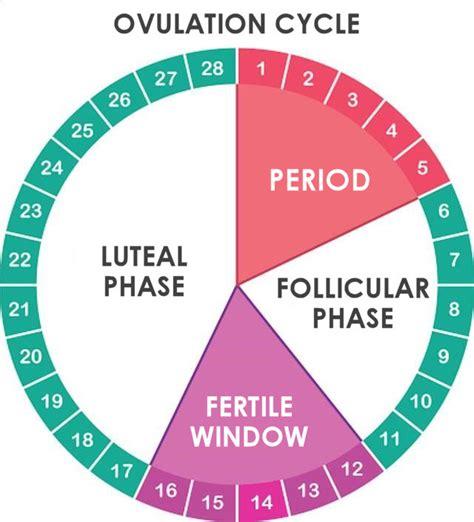
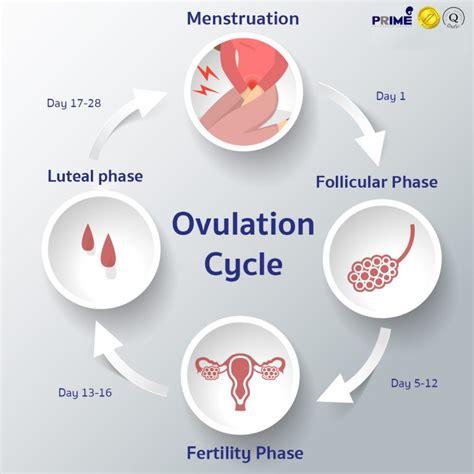
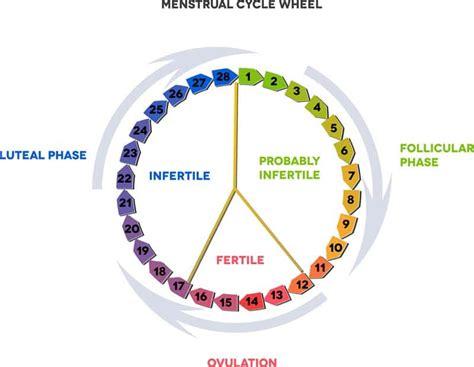
Ovulation typically occurs in middle of a woman's menstrual cycle, around day 14 in a 28-day cycle. However, this timing can vary from woman to woman, and even from cycle to cycle. This phase marks release of a mature egg from ovary into fallopian tube, where it awaits fertilization.
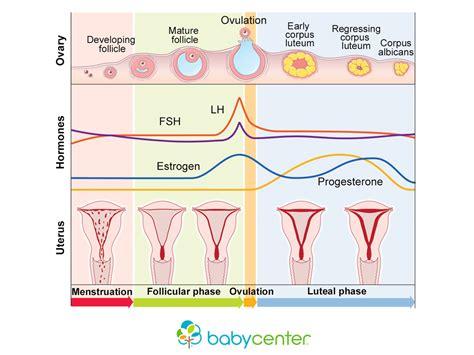
The triggers for ovulation involve complex hormonal interactions. The hypothalamus, a region in brain, produces a hormone called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH signals pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
FSH stimulates growth and maturation of follicles, which are fluid-filled sacs in ovaries that contain eggs. As follicles develop, they produce estrogen, a hormone that prepares uterus for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. This rise in estrogen triggers LH production.
A industrie panel pc touch surge in LH levels, often referred to as LH surge, triggers ovulation. The mature follicle ruptures, releasing egg into fallopian tube. The released egg is viable for fertilization for about 12-24 hours.
Detecting signs of ovulation is essential for individuals and couples trying to conceive. Several methods can help determine when ovulation is most likely to occur. These include tracking changes in basal body temperature, monitoring changes in cervical mucus, using ovulation predictor kits, and consulting with healthcare professionals.
Basal body temperature (BBT) tends to rise slightly after ovulation due to production of progesterone, a hormone that prepares uterus for pregnancy. By measuring BBT daily, individuals can identify a pattern of temperature changes that indicates ovulation has occurred.
Cervical mucus changes throughout menstrual cycle, becoming thin, slippery, and transparent during ovulation. This change in consistency allows sperm to travel easily through cervix and into uterus.

Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) are available over-the-counter and detect LH surge in urine. These kits enable women to anticipate ovulation by tracking hormone levels.
Consulting with healthcare professionals is also crucial for understanding ovulation. Doctors can conduct blood tests and ultrasound scans to identify hormonal changes and follicle development that occur during menstrual cycle.
In conclusion, understanding science of fertility and ovulation is crucial for individuals and couples planning to conceive. Recognizing signs and timing of ovulation can greatly increase chances of successful pregnancy. Through various methods like tracking BBT, monitoring cervical mucus, using OPKs, and seeking medical advice, individuals can enhance their understanding and take proactive steps towards achieving their reproductive goals.